HUABIO Blog
Experimental Tips | Doing This Step Could Boost Your Western Blot Success Rate by at Least 50%!
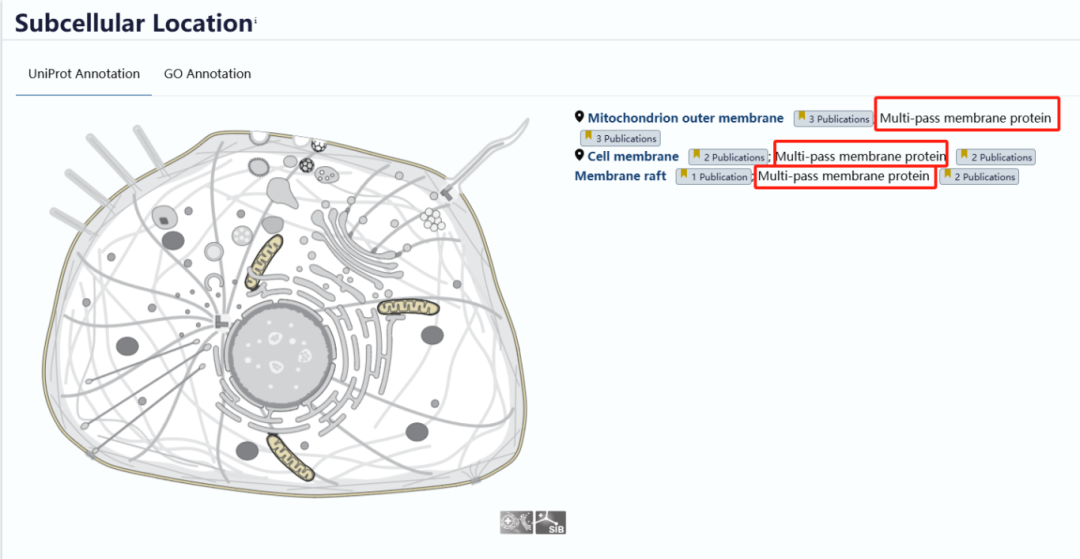
Western blot, also known as protein immunoblotting, is a commonly used experimental technique in molecular biology, biochemistry, and immunogenetics. Its fundamental principle involves using specific antibodies to stain cell or biological tissue samples that have undergone gel electrophoresis. By analyzing the positions and intensities of these stained bands, researchers gain information about the expression levels of specific proteins within the samples. Although Western blot is considered a basic experimental technique, performing it successfully is not always easy. Given its numerous steps and lengthy procedure, every stage of the protocol is critically important.
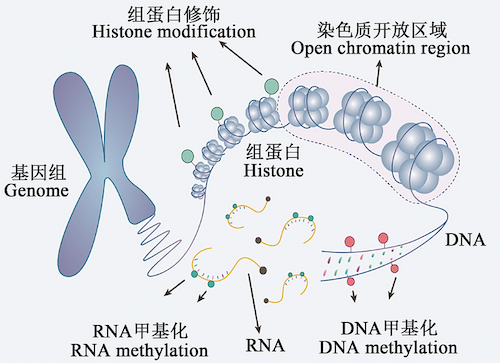
Histone Modifications: The “Regulatory Switch” for Gene Expression
In our cells, DNA is not isolated but tightly wound around protein complexes called histones, forming chromatin structures. Histones are not merely packaging materials for DNA; they play a critical role in regulating gene expression. Histone modifications involve the enzymatic addition or removal of chemical groups to specific amino acid residues on histones, changing their charge and conformation. These modifications affect the interaction between DNA and histones, thus influencing chromatin compaction and gene activation or repression.
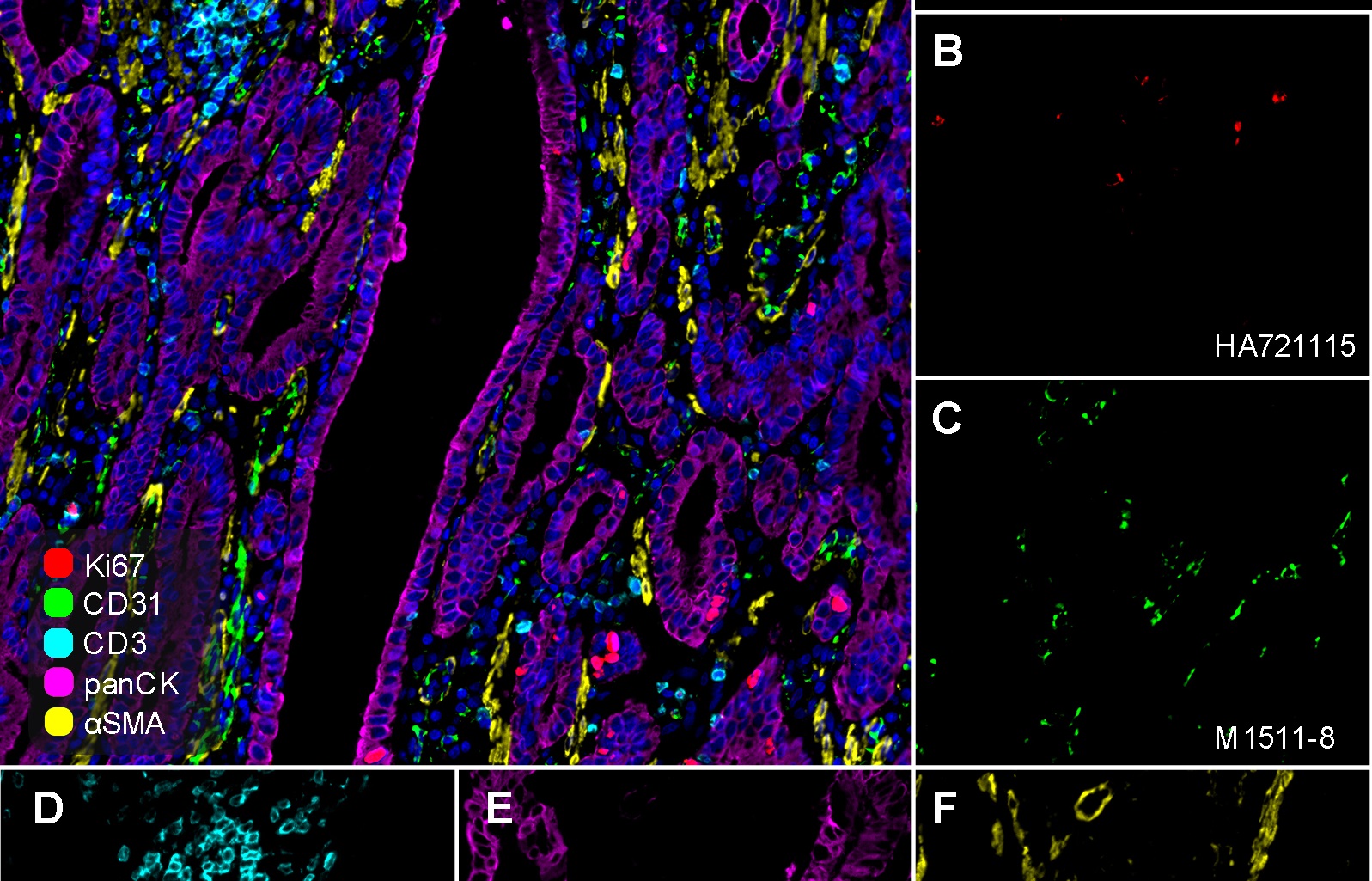
Multiplex Immunohistochemistry (mIHC) Experimental Guide: Selecting Appropriate Antibodies
Whether using conventional single-target standard immunohistochemistry (IHC) or multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC), high-quality and highly specific antibodies are crucial. Huabio provides a range of antibodies validated specifically for mIHC. Regardless of whether you are new to mIHC experiments or an experienced researcher looking to confirm your current methods, you can rely on Huabio's products and services.